Marine Conservation Volunteer Q&A
Author: Alex Oelofse, Social Media Intern & Photographer
Arthur decided to share some of his thoughts and experiences from his time at MRCI’s Turtle Cove Camp where he partook in the Marine Conservation Program.
So Arthur where are you from?
Hampshire, England.
How did you come across MRCI?
I decided to embark on something new and thought volunteering would be a great opportunity to do something like that. So I searched through many volunteering places online and came across MRCI, which was the most appealing option for me as it had the marine aspect as well as the diving.
What was your best moment?
Oh, most definitely becoming survey ready, and my weekend trip to Nosy Iranja.
So, what exactly does it entail to become survey ready?
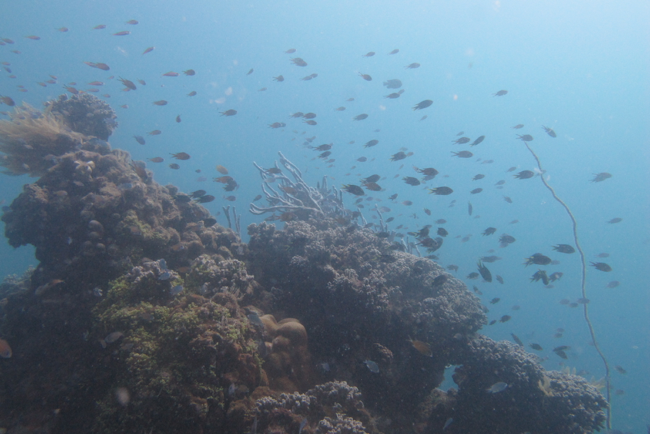
Ah, let me explain. So, there are three avenues if you can call it that; Sessile, Benthic and Active Swimmers. Sessile is made up of corals, sponges, algae, essentially living organisms that don’t move. Benthic is made up of crustaceans and bottom feeders. Lastly active swimmers include all fish. So those are the three options one has to choose from and I chose Sessile.
To become survey ready entails a process of acquiring your advanced diving qualification in order to maintain perfect buoyancy during a survey to avoid damage to the marine life that we are trying to protect. I personally did 5 point out dives to become practice survey ready, which was followed by two practice survey dives. All the data we capture is then shared with our partners CNRO (Centre National de Recherches Océanographiques) and CORDIO (Coastal Oceans Research and Development in the Indian Ocean).
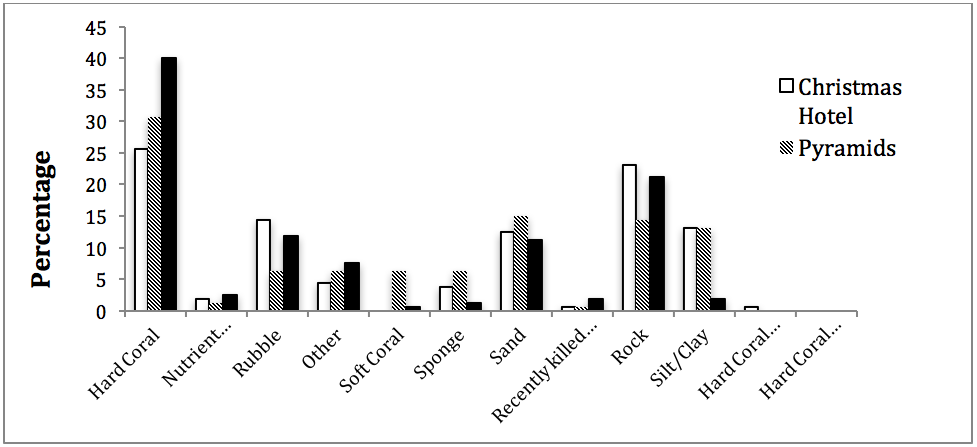
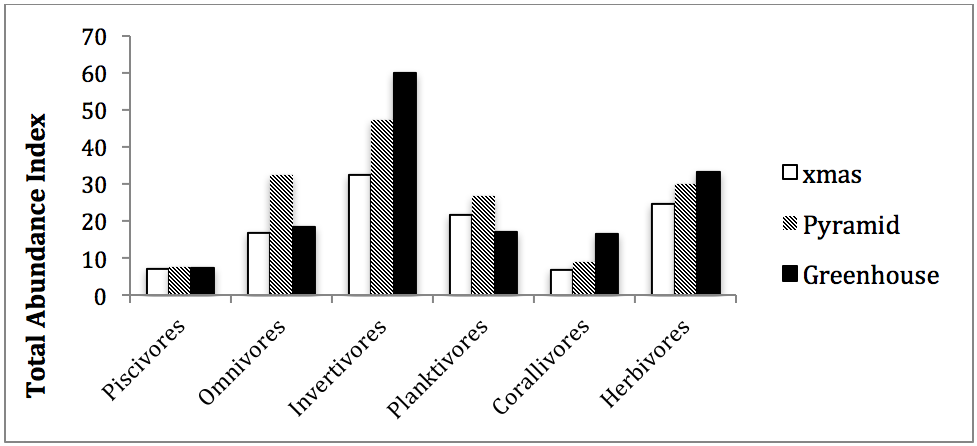
We have three sites at which we conduct these surveys including Turtle Towers, Dragons Den and Galaxea. Turtle Towers is a MPA (Marine Protected Area), which was established in 2016 with all the presidents of Nosy Komba agreeing to it being a no take zone. The data from the surveys are then compared to see how the un protected reefs are doing as opposed to the protected reefs.
Is there anything you would’ve done that you haven’t yet?
I can’t actually think of anything I have enjoyed every minute and the marine program is so well structure I was very satisfied with that.
What are your plans after this?
I will be going straight back to England where I will get a part time job as a waiter/bartender at the restaurant where I used to work. After that I will start University in September.
What are the biggest lessons that you have learnt during your time here?
Patience, most definitely patience. Never judge a book by it’s cover, in particular people. At the same time the journey might not be so great, but the destination might be incredibly worth it.
Be versatile. I would also say I have grown a lot as a person, especially my confidence I have also become more down to earth … I feel alive! I found a bit more purpose in life, not simply my old boring routines back home, best way in which I could describe this is living life in 4K resolution. Lastly I would highly recommend this to anybody!